Time:2022-11-18 Preview:
OSI 7-layer model
Application layer: provide network services for applications.
Presentation layer: provides encoding and conversion functions for application layer data.
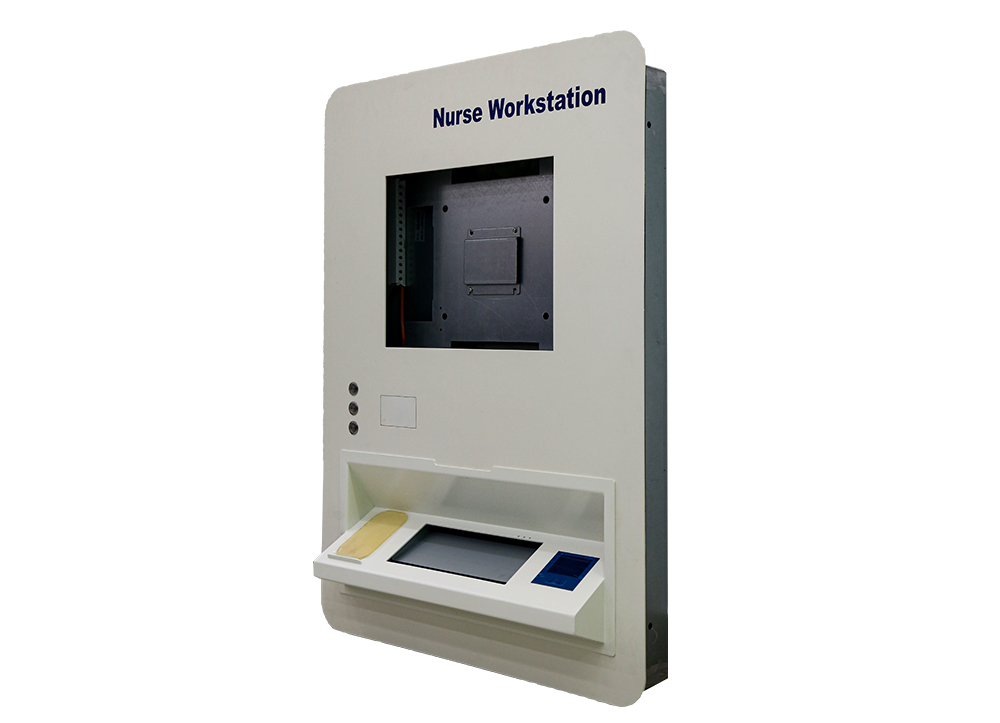

Session layer: responsible for establishing, managing and terminating communication sessions between presentation layers.
Transport layer: provides error detection before connection oriented or non connection oriented data transmission and retransmission.
Network layer: provide the router with a logical address to determine the path.
Data link layer: It controls the communication between the network layer and the physical layer.
Physical layer: transfers bit streams between devices.
TCP/IP five layer model
Application layer: BGP, DHCP, BFD, SNMP, MPLS LDP and other protocols.
Transport layer: TCP, UDP and other protocols
Network layer: mainly IP protocols, as well as IPSec, GRE, VRRP, OSPF, ICMP, PIM, IGMP and other protocols.
MPLS layer: MPLS, ARP, LACP, STP/RSTP/MSTP, IS-IS and other protocols.
Link layer: VLAN, PPPoE, PPP, HDLC and other protocols
 Related News
Related News·What precautions does the hardware spraying factory have when using the hardware spraying machine? ·CNC parts processing process process process is excessively decentralized ·Working principle of metal powder coating ·Analyzing the differences between mechanical processing and CNC machining ·Enhance the four methods of the quality of the surface layer of CNC parts ·Explain the benchmark selection of processing and positioning of the processing center? ·How does the large Dragon Gate Processing Center and the vertical processing center distinguish? ·What are the characteristics of vertical CNC machining centers? ·What is a CNC lathe ·Hardware die-casting process


